Sometimes, it takes years or months for certain events to unfold and reveal their full-scale magnitude and long-term effects. However, others take just only a day to make a major impact on humankind and the course of history. So it goes for the accident that took place at the Chernobyl nuclear power station on the 26th of April 1986, permanently altering that region and making the area around the former plant uninhabitable for an estimated 20,000 years. Initially denied as having happened by the Soviet authorities, the disaster is now considered the worst of its kind in history.
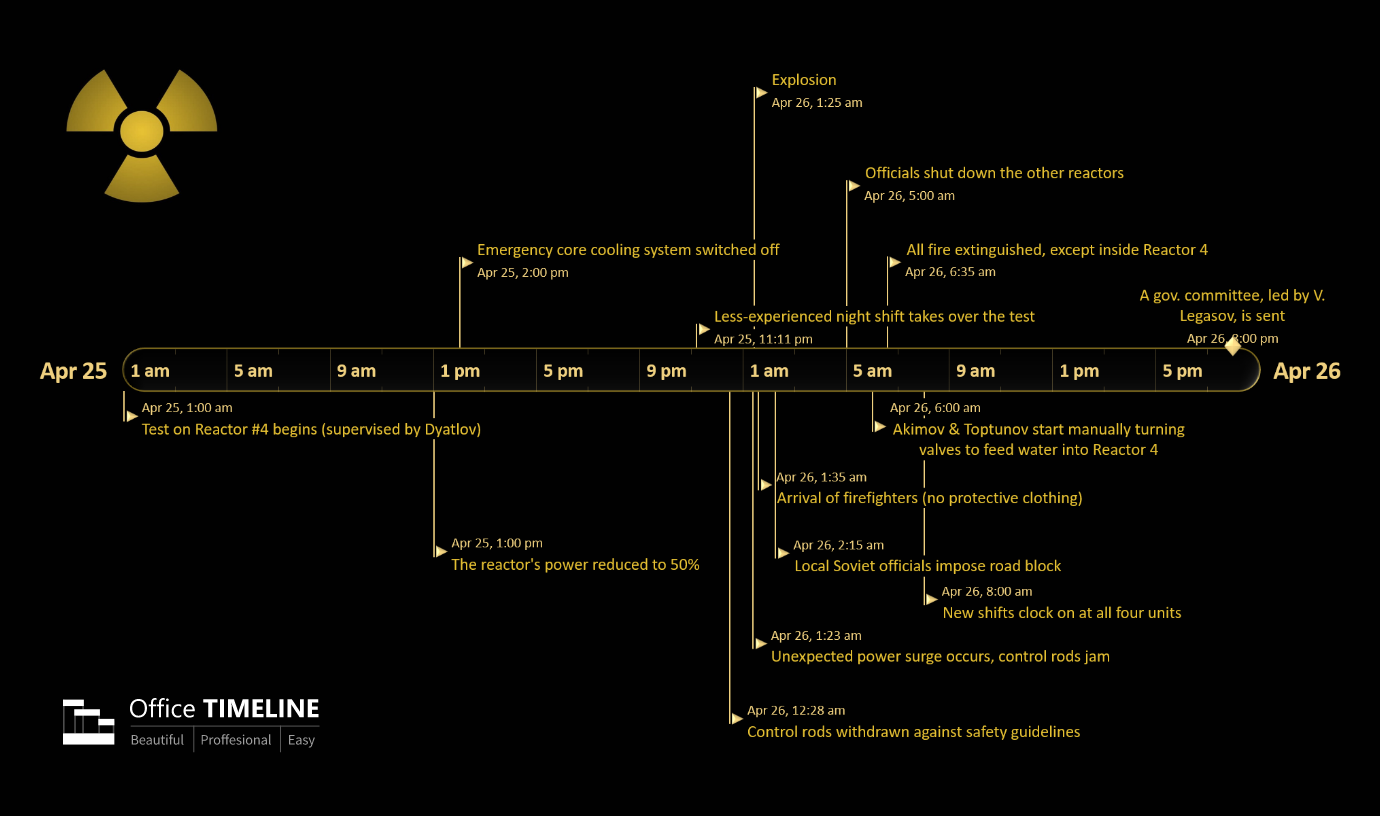
To illustrate how the Chernobyl nuclear accident escalated to a historic calamity, we created The Chernobyl Disaster Timeline, which gives a blow-by-blow narrative of the missteps that triggered this tragic meltdown.
Background Facts
- The nuclear accident occurred at the V.I Lenin Nuclear Power Station, near the city of Chernobyl (65 miles north of Kiev, Ukraine), in the former URSS.
- The Chernobyl nuclear power plant was considered a model of Soviet engineering, using four RBMK nuclear reactors to produce electricity for about 30 million homes and businesses.
- The power plant’s newest reactor (the fourth one) was the scene of the tragedy. It contained 1,600 radioactive uranium-235 fuel rods. Due to the unstable nature of U-235, its atoms are capable of releasing neutrons that hit other U-235 nuclei, which in turn release new neutrons. All this causes a chain reaction, the byproduct of which is the release of huge quantities of heat and energy which are used to turn water into steams. The steam then drives a turbine, thus generating electricity.
- To contain the chain reaction within limits, control rods made of a neutron-absorbing substance need to be inserted between fuel rods. For Reactor No. 4’s control rods (a total of 211), the element boron was used. Raising the control rods leads to the acceleration of the chain reaction, while the lowering of the control rods causes the chain reaction to slow down.
- Ironically, it was a safety test that brought about the destruction. Coinciding with a routine downtime for maintenance, the test was scheduled to determine whether the reactor could still be cooled in case of a power failure. In preparation for this process, Chernobyl’s operators initiated power reduction on the 25th of April (1:00 pm) and, after twelve hours, Reactor No. 4 reached 50% power. According to the standard procedures of the safety test, the required threshold was of 30%. However, due to an apparent need for electricity in the region, the Soviet authorities called for the reactor to remain at 50% for another 9 hours. Meanwhile, the emergency core cooling system was switched off…
- With power plummeting far below the level at which the reactor would be stable, operators were asked to remove almost all control rods against safety guidelines. The violation of these protocols led to a sudden power surge inside the plant. Despite the attempt to shut down the reactor altogether, control rods jammed upon entering the core, causing a series of explosions inside and then the final one, that literally blew apart the reactor and the 1,000-ton roof above it, spewing radioactive material into the atmosphere.
Killing 31 people directly (28 workers and firefighters dying of acute radiation poisoning), the Chernobyl calamity is considered responsible for thousands of premature cancer deaths as well. Encased in a massive steel structure deployed in 2016, the remains of the reactor still require containment and monitoring efforts, with its cleanup expected to last until at least 2065.
The Chernobyl Disaster Timeline was built with Office Timeline, a user-friendly add-in that helps you easily produce clear and beautiful timelines and other types of visuals right inside PowerPoint. The slide is free to share and copy, and can be edited and updated using the Plus version of the tool.
Download the Chernobyl Disaster Timeline for PowerPoint here.
Turn project data into professional timelines
Get the advanced features of Office Timeline Pro+ free for 14 days.
Get free trial